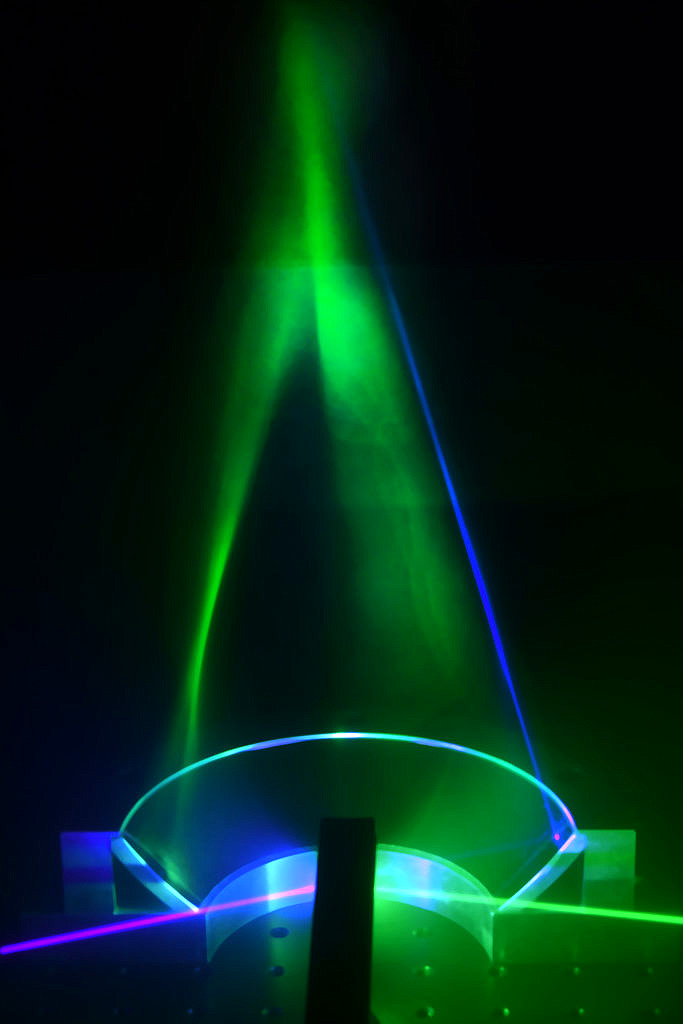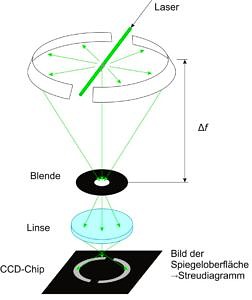
In this research topic we employ Elastic Light Scattering (ELS) for the characterization of Nanoparticle aggregates. In conventional methods the angular dependent scattered light is either detected using multiple detectors at fixed scattering angles or by one detector being rotated on a goniometer. In the first case of a few fixed detectors only a limited number of angles can be measured, using a single detector on a goniometer only allows for the measurement of stationary processes due to the long measurement procedure.
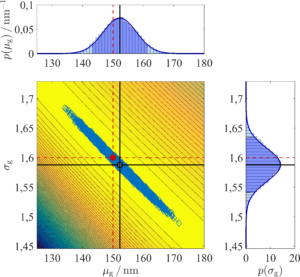
The newly developed measurement principle Wide-Angle Light Scattering (WALS) employs an ellipsoidal mirror simultaneously imaging the scattered light from a wide angular range onto a camera chip with a high angular resolution. This allows for a determination of aggregate size and morphology from a single camera frame. With WALS not only turbulent combustion processes can be investigated, but also an online surveillance of industrial particle production processes, like production of carbon blacks or silica particles, is possible. Furthermore, the high angular resolution allows for an inverse analysis of the scattering data to obtain parameters of the particle size distribution.
By a combination with other measurement techniques, such as Laser-Induced Incandescence, a comprehensive characterization of gas borne nanoparticles can be achieved.
Literatur
- , , , :
In Situ Determination of Droplet and Nanoparticle Size Distributions in Spray Flame Synthesis by Wide-Angle Light Scattering (WALS)
In: Materials 14 (2021), Article No.: 6698
ISSN: 1996-1944
DOI: 10.3390/ma14216698 - , , , :
Droplet sizing in spray flame synthesis using wide-angle light scattering (WALS)
In: Applied Physics B-Lasers and Optics 126 (2020), Article No.: 92
ISSN: 0946-2171
DOI: 10.1007/s00340-020-07443-2 - , :
Characterization of a silica-aerosol in a sintering process by wide-angle light scattering and principal component analysis
In: Journal of Aerosol Science 119 (2018), p. 62-76
ISSN: 0021-8502
DOI: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2018.02.006

