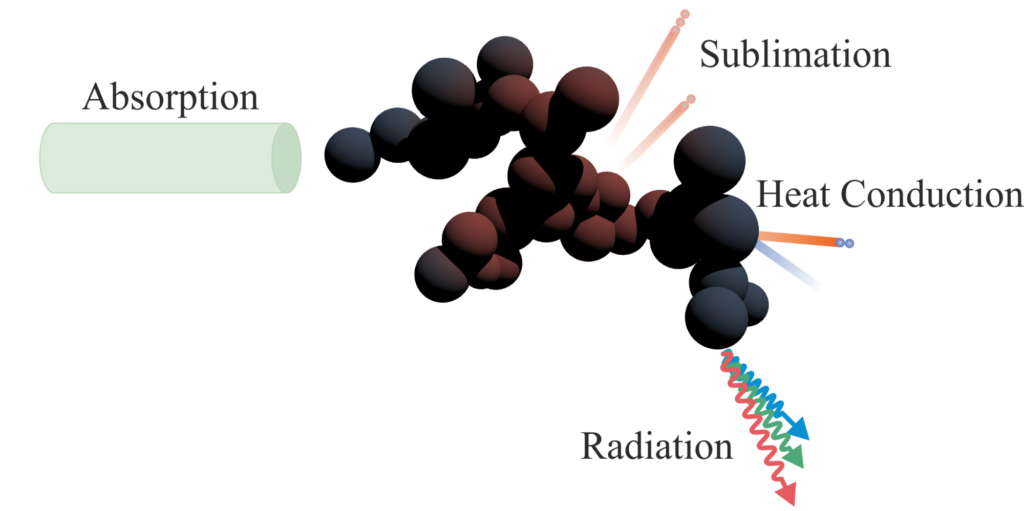
Laser Induced Incandescence (LII), which in large parts was co-developed at LTT, allows for an in-situ determination of primary particle size and volume fraction of gas borne nanoparticles. A very short laser pulse is absorbed by the particles, increasing their internal energy. The enhanced thermal radiation signal and the temporal cooling behavior is detected and analyzed. Applying sophisticated physical models the particle size and concentration can be determined.
LII has proven to be an outstanding tool for the characterization of soot particles in various combustion processes. Depending on the application the technique can either be used point-wise or for 2D imaging. LII is mainly employed to investigate soot formation in model flames and engines but also for in-situ measurements in engine exhaust gases and for carbon black characterization. Furthermore LII can also be used with nanoparticles made from other materials, depending on the thermodynamical and optical properties of the material.
Besides fundamental investigations on the detailed processes proceeding during LII current research projects work on the combination with other measurement techniques (e.g. Elastic Light Scattering) for a comprehensive characterization of nanoparticles and particle aggregates.
Literatur
- , , , , :
Three-dimensional particle size determination in a laminar diffusion flame by tomographic laser-induced incandescence
In: Applied Physics B-Lasers and Optics 127 (2021), Article No.: 4
ISSN: 0946-2171
DOI: 10.1007/s00340-020-07562-w - , , , :
Can soot primary particle size distributions be determined using laser‑induced incandescence?
In: Applied Physics B-Lasers and Optics 125 (2019), Article No.: 109
ISSN: 0946-2171
DOI: 10.1007/s00340-019-7219-7 - , , :
A mobile system for a comprehensive online-characterization of nanoparticle aggregates based on wide-angle light scattering and laser-induced incandescence
In: Review of Scientific Instruments 87 (2016)
ISSN: 0034-6748
DOI: 10.1063/1.4948288